Most people are familiar with Kate Grenville’s novel, published in 2005 and shortlisted for the 2006 Booker Prize. It features a convict called William Thornhill, a Thames boatman transported for life to New South Wales for stealing timber, whence he travels with his wife and two young boys and where, on receiving his absolute pardon, he sets his sights on a patch of land on the Hawkesbury River north of Sydney and then has to contend with the indigenous people whose land he is purloining.

It was apparently the idea of Cate Blanchett and Andrew Upton, then Artistic Directors of the Sydney Theatre Company, to adapt the book into a stage play, for which purpose they hired the services of the playwright Andrew Bovell. The result, realised by director Neil Armfield, designed by Stephen Curtis and set in a quarry outside Adelaide, is one of the most memorable nights I have ever spent at the theatre.
Ms Grenville always stated she felt unable to tell her story from the point of view of the indigenous people, which is why they are shadowy entities in her book – always there but not quite defined. The same is not the case in the play. The Aboriginal people Thornhill is so afraid of are there in flesh and blood, speaking Dharug, the local language of the Hawkesbury – which, wisely I think, is not translated, so we the audience are as confused and perhaps as scared as Thornhill and his wife.
The play is narrated by a character called Dhirrumbin (Dharug for the Hawkesbury River). Played by Ningali Lawford Wolf she tells the story with a mixture of anger, regret and ruefulness. Never have I seen the misunderstandings between two cultures so vividly, humorously and ultimately tragically portrayed. When Thornhill in one scene confronts an Aboriginal elder and tells him forcibly to ‘go away’ the elder responds with what I assumed to be the same instruction in his own language, to which Thornhill replies, with relief, ‘Well at least we understand each other’. The massacre is portrayed twice: once from the white point of view, where we watch an advancing line of men with guns puffing on white powder (flour I think) to portray the musket shots – a wonderfully imaginative moment. Then, separately, we see the Aboriginal people, children and women among them, drop one by one to the ground so all this is left is a single wounded Aborigine.
The Anstey Hill Quarry, some distance out of Adelaide, is where the stone for the city’s first public buildings was excavated back in the 19th century. The play is set on a wide open stage with a painted floorcloth and a sheer cliff as backdrop. Live music is composed and performed by Iain Grandage on piano and cello, with the occasional addition of guitar and pipe; lights are set on scaffolding on either side of the stage. All in all a magical setting you could say, enhanced by uniformly supreme performances from the entire cast.

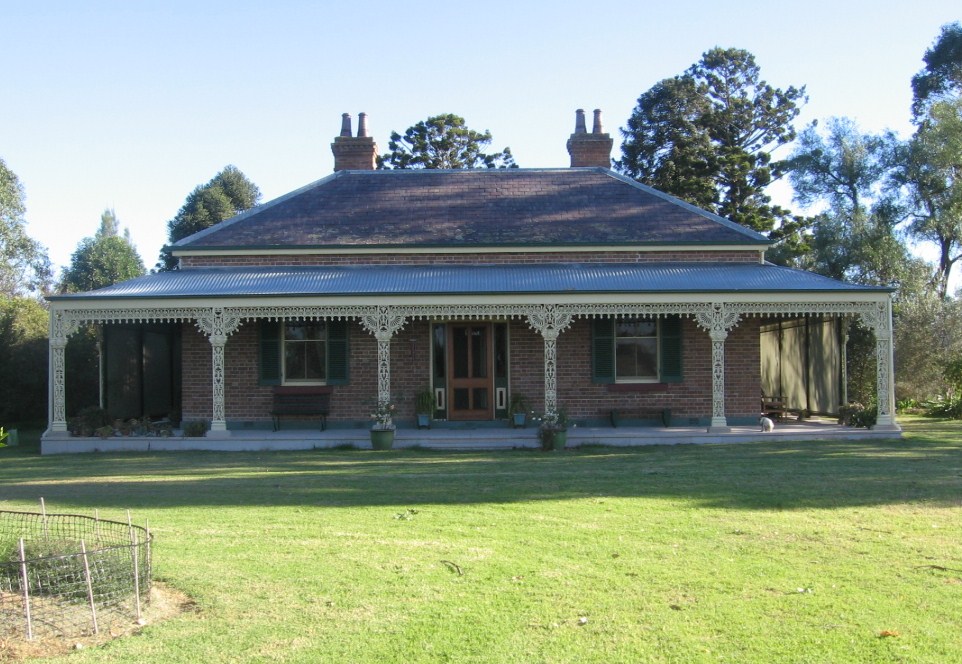
I have a particular interest in the play of course as my own ancestors, featured in my book The Worst Country in the World, were granted land not far upstream from the fictional Thornhill* and his family, and at much the same time. They were the lucky ones, they did not have to fight for what they considered their ‘official’ right to the land; which would not have made a scrap of difference to the indigenous local people of course, to whom an interloper was an interloper.
The subject of the British invasion of New South Wales is a sensitive one, to say the least. But with a mixture of humour, compassion and even-handedness this presentation of The Secret River achieves the near-impossible: by focusing on one family in one place at one time it manages to encapsulate the much bigger story of western colonisation of Australia
Miraculous. What I want to know now is when will we colonisers have the chance to see this wonderful production back in the UK? National Theatre, I hope you are reading this.
*Yet based loosely on Grenville’s great x 3 grandfather Solomon Wiseman.